Interest rates play a crucial role in the functioning of the U.S. markets. They have a profound impact on various sectors and industries, influencing the economy as a whole. In this article, we will explore how interest rates affect the U.S. markets and what it means for investors and consumers.
1. Bond Market
The bond market stands as a primary arena where the impact of interest rates is keenly felt. Bonds, as debt instruments, are intricately linked to prevailing interest rates. When interest rates rise, newly issued bonds offer higher yields, diminishing the attractiveness of existing bonds with lower rates. Consequently, bond prices decline, reflecting the inverse relationship between bond prices and yields. Conversely, when interest rates decline, bond prices tend to rise as investors seek higher returns in a low-rate environment.

2. Stock Market
The stock market is also influenced by changes in interest rates. When interest rates are low, borrowing costs for companies decrease, making it cheaper for them to finance expansion and investment. This stimulates economic growth and increases corporate earnings, which in turn boosts stock prices. Conversely, when interest rates rise, borrowing costs increase, reducing the profitability of businesses and dampening investor sentiment. Higher interest rates also make bonds more attractive relative to stocks, diverting investment away from equities.
3. Real Estate Market
Interest rates have a significant impact on the real estate market. Mortgage rates, which are directly influenced by long-term interest rates, play a crucial role in determining housing affordability. When interest rates are low, mortgage payments become more affordable, leading to increased demand for homes. This drives up home prices and boosts construction activity. Conversely, when interest rates rise, mortgage rates also increase, making housing less affordable. This can lead to a slowdown in the real estate market and a decline in home prices.
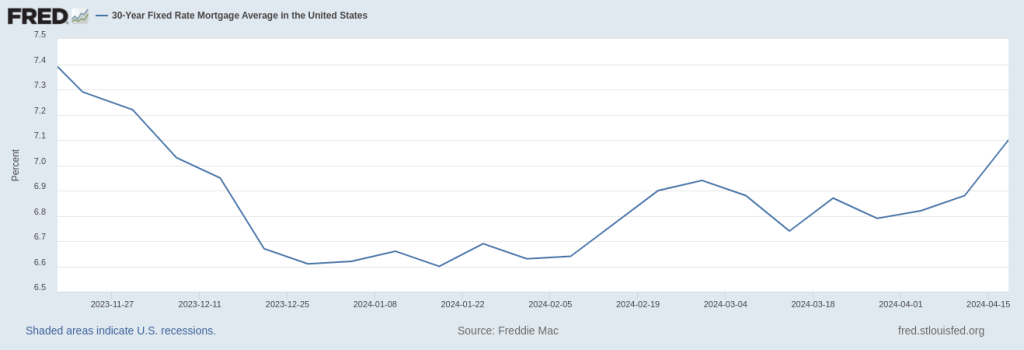
4. Consumer Spending
Changes in interest rates also affect consumer spending. When interest rates are low, borrowing costs decrease for consumers, making it easier to obtain credit for large purchases such as homes, cars, and appliances. This stimulates consumer spending and drives economic growth. On the other hand, when interest rates rise, borrowing costs for consumers increase, making it more difficult to access credit. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, which can have a negative impact on the economy.
5. Currency Exchange Rates
The relationship between interest rates and currency exchange rates is complex but significant. When interest rates rise, the currency of that country tends to appreciate as foreign investors seek higher returns. This can make exports more expensive and imports cheaper, leading to a decrease in the country's trade balance. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the currency tends to depreciate, making exports more competitive and imports more expensive.
In conclusion, interest rates have far-reaching effects on the U.S. markets. They impact the bond market, stock market, real estate market, consumer spending, and currency exchange rates. Understanding how these relationships work can help investors and consumers make informed decisions. Keep an eye on interest rate changes as they can provide valuable insights into the direction of the economy and market trends.